We design networks that grow with your business, fast, reliable, and always secure.
Network design is the practice of planning and designing a communications network.
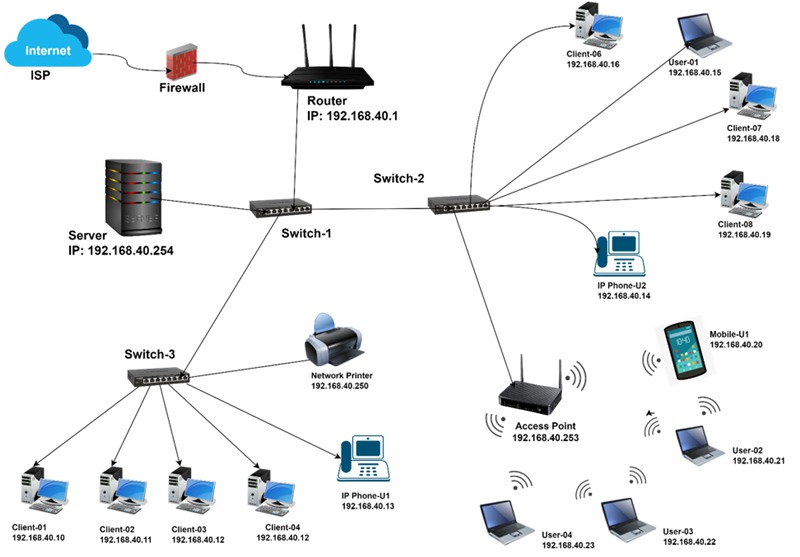
That process starts with identifying business and technical requirements and continues until just before the network implementation stage (when you actually do the work to deploy and configure what was designed). Network analysis, IP addressing, hardware selection, and implementation planning are all part of network design.
In simple networks, like those found in most homes and small offices, network design is a straightforward process. In large enterprise networks, the network design process is often very complex and involves multiple stakeholders.
In the context of network design, a network lifecycle model helps explain where and how network design fits into the broader lifespan of your network’s components and overall structure.
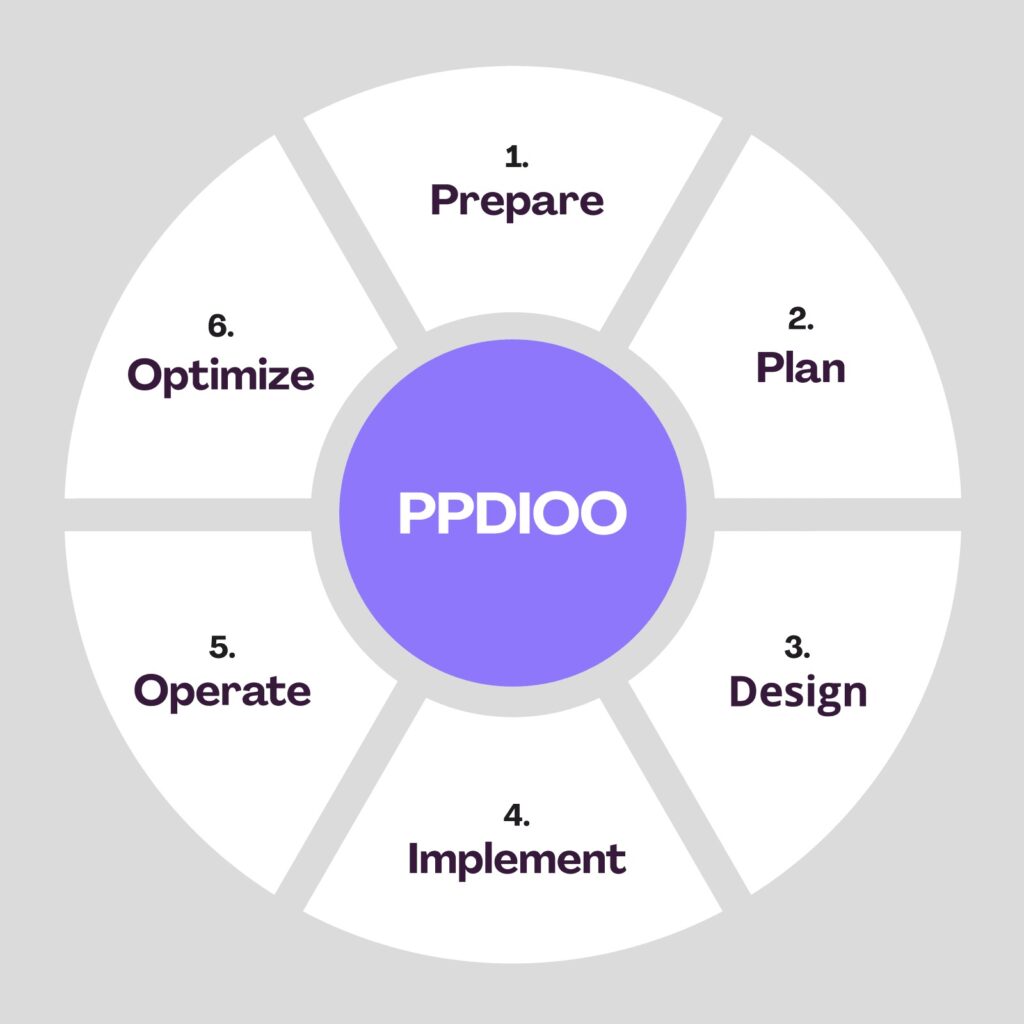
One of the most popular network lifecycle models is Cisco’s PPDIOO (Prepare, Plan, Design, Implement, Operate and Optimize) model:
This is where you define high-level requirements and strategy. For example, your deliverables from this phase may include requirements documentation and current state surveys.
This stage deals with specific network requirements based on information gathered in the planning stages.
During the design stage, the information gathered from the previous two stages is used to create a detailed network design.
This is where the work gets done to configure and deploy the network infrastructure. There is often testing to validate the design in this phase.
This is the portion of the lifecycle where the network is in production use. During this stage, monitoring is an important part of validating that the network is working as designed and being able to quickly address issues when it isn’t.
At some point in most networks’ lifecycle, tweaks and optimizations are needed. This is the stage where those changes are identified. For major changes, the cycle begins again to plan and implement them.

Have a question or need IT support? Reach out to our team, we’re ready to help you with reliable, fast, and personalized service.
© 2018 – Microsys Computer Solutions, LLC